
Wi-Fi 6E, also known as Wi-Fi 6 Extended, is an extension of Wi-Fi 6 technology that operates in the 6 GHz frequency band. This frequency band was previously reserved for military and scientific purposes, but it is now available for commercial use.
The 6 GHz band opens up a massive 1,200 MHz of spectrum, compared to 500 MHz in the 5 GHz band used by Wi-Fi 5 and Wi-Fi 6. With more available spectrum, Wi-Fi 6E can offer faster maximum speeds of 9.6 Gbps, reduced latency, and support for many more connected devices at once. The 6 GHz band is also less crowded with other wireless technologies, enabling higher performance and reliability.
Besides, Wi-Fi 6E also uses advanced technologies like MU-MIMO (Multi-User Multiple Input Multiple Output) and beamforming to enhance network performance and reliability.
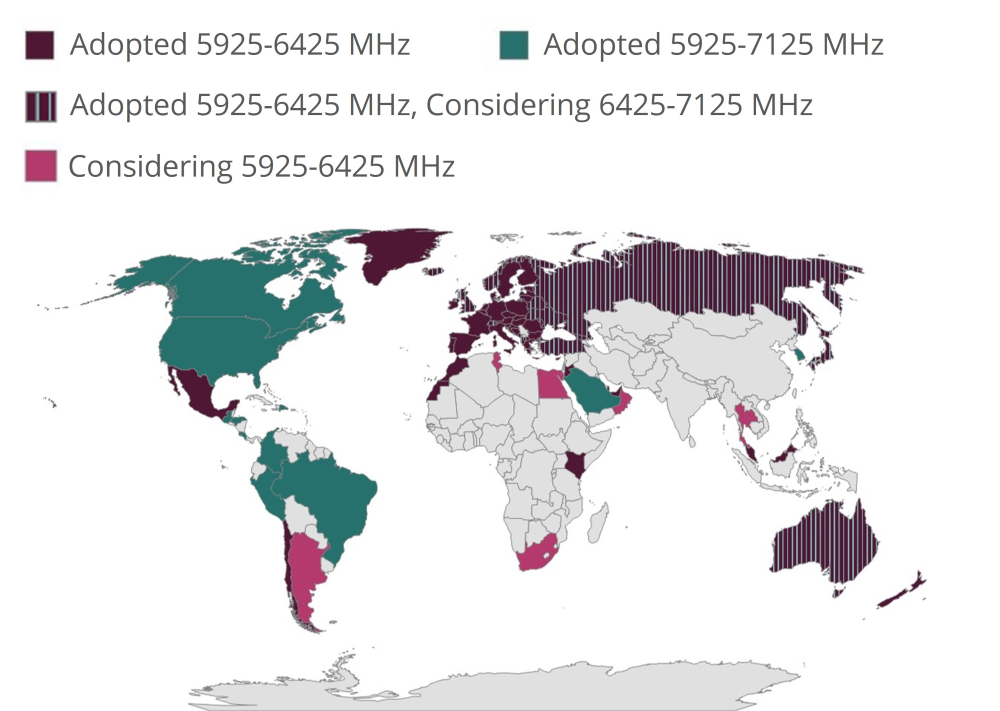
Image source: Wi-Fi Alliance
Wi-Fi 7 is the next-generation standard of Wi-Fi technology, which has not been officially released yet. However, Wi-Fi 7 is already regarded as one of the main directions for the future development of Wi-Fi technology.
Note: The 802.11be amendment is currently in development, with an initial draft released in March 2021 and a projected final version anticipated by early 2024.
Both Wi-Fi 6E and Wi-Fi 7 support more device connections and provide better network connectivity stability. These technical features help improve wireless network performance and user experience.
In terms of security, both Wi-Fi 6E and Wi-Fi 7 support WPA3, the latest encryption standard for wireless networks. WPA3 provides stronger security protocols such as stronger password-based authentication and forward secrecy, which ensures that even if attackers successfully obtain the network password, they cannot use it to decrypt past network traffic.
From a technical standpoint, Wi-Fi 6E and Wi-Fi 7 have some differences. Wi-Fi 6E mainly improves the use of the 6GHz frequency band, providing higher network capacity and faster network speeds. Wi-Fi 7, on the other hand, improves the use of higher frequency bands, providing higher transmission rates and lower network latency.
As the next major upgrade after Wi-Fi 6E, Wi-Fi 7 will provide maximum theoretical speeds up to 46 Gbps, less than 1 millisecond latency, and support for a massive number of devices at once. These capabilities will help enable new high-bandwidth, low-latency applications that aren't possible even with Wi-Fi 6E.
Wi-Fi 6E
Wi-Fi 7
Launch date
2021
2024 (expected)
IEEE standard
802.11ax
802.11be
Max data rate
9.6 Gbps
46 Gbps
Bands
2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, 6 GHz
2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, 6 GHz
Channel size
20, 40. 80, 80+80, 160 MHz
Up to 320 MHz
Modulation
1024-QAM sOFDMA
4096-QAM OFDMA (with extensions)
MIMO
8x8 UL/DL MU-MIMO
16x16 UL/DL MU-MIMO
RU
RU
Multi-RUs
MAC
/
MLO
As you can see, Wi-Fi 7 is more advanced than Wi-Fi 6E in several ways, the most significant being speed.
Wi-Fi 7 can deliver speeds in excess of 40Gbps, more than three times faster than Wi-Fi 6E. Besides, Wi-Fi 7 doubles the bandwidth of the previous generation by fully utilizing the 6 GHz band and allows for faster simultaneous transmissions by extending channel width to 320 MHz.
Wi-Fi 7's higher-order modulation scheme, 4096-QAM, enables symbols to carry 12 bits instead of 10 bits, resulting in a 20% theoretical transmission rate increase compared to Wi-Fi 6E's 1024-QAM. This leads to higher transmission efficiency, allowing for smooth streaming of 4K/8K videos, online gaming without lag, and seamless live streaming from home computers.
Additionally, Wi-Fi 7 supports 16×16 UL/DL MU-MIMO (multi-user, multiple-input, multiple-output) functionality, which means more users can send and receive data simultaneously. This is particularly important in crowded public places or apartment buildings. With MU-MIMO, Wi-Fi 7 can provide more efficient and reliable connections for all users.
Wi-Fi 6E and Wi-Fi 7 are prominent players in the evolving world of wireless connectivity, offering enhanced capabilities to meet the growing demands of diverse usage scenarios. Let's explore their applications and how they revolutionize digital connectivity and communication.
Currently, Wi-Fi 6E has been widely applied in various scenarios, such as public places like enterprises, schools, hospitals, hotels, shopping malls, as well as private places like homes and offices. Among them, enterprises are one of the main application scenarios for Wi-Fi 6E. Wi-Fi 6E can provide higher network capacity and faster network speeds, meeting the needs of high-density device access in enterprises, and providing more stable network connectivity.
Besides, Wi-Fi 6E can also be applied in scenarios like video conferencing, remote work, cloud computing, providing more efficient network connections and more stable service quality.
In addition, with the rapid development of 5G technology, Wi-Fi 6E will also become an important complement to future 5G wireless networks. By combining Wi-Fi 6E with 5G, faster, more stable, and more reliable wireless network transmission can be achieved, bringing people a better wireless network experience.
Moreover, Wi-Fi 6E technology can also provide strong support for the development of the future Internet of Things (IoT). With a large number of IoT devices and a huge amount of data to transmit, traditional Wi-Fi technology will find it difficult to meet the demand. Wi-Fi 6E technology, however, can provide higher capacity and faster transmission speeds to support the development of IoT.
In terms of market opportunities, Wi-Fi 6E has already begun to gradually popularize. It is expected that in the next few years, the commercial application of Wi-Fi 6E technology will continue to expand and the application scenarios will become more widespread. According to market research institutions, the market size of global Wi-Fi 6E devices is expected to exceed 3 billion US dollars by 2026. Therefore, Wi-Fi 6E has huge market potential and will be one of the important development directions in the wireless network field in the future.
Wi-Fi 7 will play an important role in higher density, higher speed, and lower latency scenarios. For example, Wi-Fi 7 can be applied in industrial automation, intelligent transportation, smart homes, and other fields to support more efficient, intelligent, and secure wireless network transmission.
Wi-Fi 7 can also provide better performance support for cloud gaming, VR/AR, and other application scenarios to meet users' demand for high-quality wireless network experience.
In terms of market opportunities, since Wi-Fi 7 has not been officially released, the market size and potential have not been specifically evaluated yet. However, with the continuous development of Wi-Fi technology and the increasing market demand, the commercial prospects and market opportunities of Wi-Fi 7 technology will gradually emerge. It is expected that Wi-Fi 7 will gradually begin commercial applications in the coming years, and the application scenarios will be even more extensive.
So, what does this mean for the future of the wireless telecommunications industry? Wi-Fi 6E and Wi-Fi 7 are expected to coexist in the market for a period of time, as the adoption of new technology often occurs gradually. However, as more devices become compatible with these new standards and the demand for faster and more reliable wireless connections continues to grow, we can expect a shift towards Wi-Fi 7 in the next few years.
For telecom operators, Wi-Fi 7 presents opportunities to enable advanced connectivity services for enterprise customers and gigabit wireless broadband. Some potential use cases include:
High-density connectivity in public venues: Stadiums, transit hubs and convention centers will require extremely high-capacity wireless networks to meet demand from thousands of concurrent users. Wi-Fi 7 can help make gigabit connectivity feasible in these dense environments.
Flexible enterprise WAN: Wi-Fi 7's high performance, low latency and massive device support will allow it to serve as an alternative or complement to wired corporate networks. Operators can deploy Wi-Fi 7 for primary or backup enterprise connectivity.
Multi-gigabit wireless broadband: In areas where fiber optic connectivity isn't available or affordable, Wi-Fi 7 point-to-multipoint networks can provide multi-gigabit internet speeds for residential broadband, especially when used with Wi-Fi mesh technology.
Support for augmented and virtual reality: Cutting-edge AR and VR applications require bandwidth in the tens of gigabits and milliseconds of latency which Wi-Fi 7 will be uniquely suited to provide. Operators can enable immersive untethered experiences with Wi-Fi 7.
With a focus on operators' strategic challenges, SDMC delivers comprehensive customization services that are perfectly adapted to their specific needs.
SDMC empowers operators to deliver exceptional home networking experiences through broadband solutions built for scale and performance. Our platform integrates fiber, DOCSIS, 5G and standards-based Wi-Fi 5 / Wi-Fi 6, 6E / Wi-Fi 7 technologies to provide whole-home coverage, ultra-fast speeds and support for data-intensive applications. Reliable, manageable and deployable, SDMC solutions simplify the path to next-generation residential services.
©2003-2026 SDMC Technology Co., Ltd